What is a Sample Conditioning System?
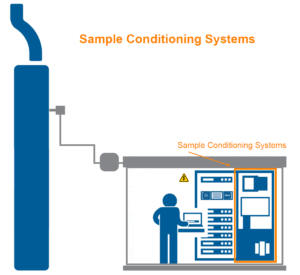
In an Extractive CEMS, the stack sample is kept heated above the acid dew point from the stack probe down to the analyzer cabinet. Because the sample is “hot and wet”, it cannot be introduced directly into the CEMS analyzers without doing damage. A Sample Conditioner is used to dry the sample before it enters the analyzers.
The Sample Conditioner being discussed is a Thermo Electric type utilizing Peltier Cooling. The sample conditioner system is located in the CEMS cabinet or shelter. It can be rack or wall mounted.
Sample Conditioning Components
A Sample Conditioner System for CEMS is made up of the following components:
- Peltier Cooler: A Peltier cooler is a solid-state active heat pump that transfers heat from one side of the device to the other side against a temperature gradient (from cold to hot), with consumption of electrical energy. It’s a very reliable system with no moving parts and virtually no maintenance.
- Sample Pump: Used to create a vacuum that draws the sample from the stack. Flow rate is typically 4-6 lpm.
- Sample Cooler: Utilizes Peltier (pelt-tee-ay’) cooler and dual impingers. Impingers are simple heat exchangers. As the sample cools in the impingers, the moisture condenses and collects. A Peristaltic pump constantly removes the condensation. Dual impingers are typically utilized where the first impinger is a “passive” impinger which cools the sample to ambient temperatures (this impinger is not cooled by the Peltier device). The second impinger is an “active” impinger which is cooled by the Peltier device and cools the sample down to 4°C. On the way out of the second impinger, the sample is heated back up to ambient temperatures vaporizing any remaining moisture in the sample where it then heads to the analyzers. For high moisture removal applications, dual “active” impingers can be used.
- Peristaltic Pump: This dual pump (one for each impinger) is used to remove the moisture as it condenses out of the sample in the impingers. A peristaltic pump is a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained within a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump casing. A rotor with 3 rollers attached to the external circumference compresses the flexible tube. As the rotor turns, the part of the tube under compression closes (or ‘occludes’) thus forcing the fluid to be pumped or move through the tube. Additionally, as the tube opens to its natural state after the passing of the cam, (‘restitution’) fluid flow is induced to the pump.
- Filter: Once through the sample conditioner, the sample passes through a final filter.
- Flow Meter: Used to adjust sample flow through the system.
- Water Carryover Sensor: Used to sense moisture breakthrough if the sample conditioner fails to operate correctly. This signal is normally sent to the Data Acquisition System (DAS) for CEMS.
Flow Path Options
In the most common system, two sample impingers are used to lower the sample temperature and remove the moisture. The first impinger (passive) cools the sample to ambient temperatures and the second impinger cooled by a Peltier Cooler (active) cools the sample to lower temperatures (typ. 4°F) removing the remaining moisture.
Figure 1: The CEMS sample pump draws the sample through the sample conditioner first so that the sample is dried before entering the pump (thereby protecting it from damage). The common method for plumbing this is shown in Figure 1 where the sample is drawn first through each impinger in series.
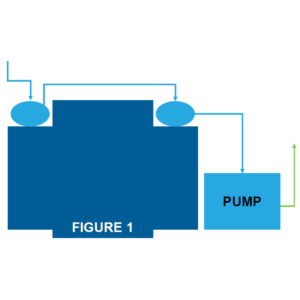
Figure 2: In order to increase moisture removal, the
system can be replumbed to draw the sample through the first impinger, then the
sample pump, and then the second impinger (Figure 2). This serves to “push” the
sample through the active impinger increasing its moisture removing ability.
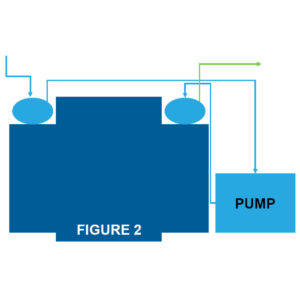
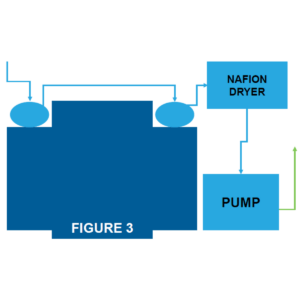
Figure 3: If implementing this plumbing scheme,
the moisture level must not be too high or the passive first impinger will
allow too much moisture into the pump which could cause damage. In this case
consider adding a PermaPure Nafion drier system in line shown in Figure 3. Figure
3 details a plumbing method which adds an additional dryer after the second
stage of the impinger. This is an excellent way to maximize the moisture
removing the ability of a sampling system.
Quarterly & Annual Maintenance
Quarterly and annual maintenance is required on sample conditioning systems.
- The sample filter must be changed quarterly.
- The sample pump should be rebuilt on an annual basis.
- The tubing used in the peristaltic pump is typically replaced annually but can be done more frequently, depending on the application.
- The impingers may require cleaning or replacing from time to time if the application is “dirty” or “corrosive”.
ESC Spectrum Can Provide Competitive Rates
Interested in learning a more comprehensive overview of how CEM Systems work? Read Understanding Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems (CEMS): A Comprehensive Guide. This guide will give you a complete understanding of all the components in the flow of a CEMS.